
Nutrition is the scientific study of how the body’s processes utilize food to maintain health, promote growth, and support overall well-being.
It encompasses various factors, including the biochemical, physiological, and ecological aspects of food. Through an understanding of nutrition, we can recognize how the essential nutrients in our diet contribute to bodily functions and influence our health outcomes. These vital nutrients primarily include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals, each playing a specific role in maintaining optimal health.
Carbohydrates are a primary source of energy for the body, crucial for fueling various cellular processes. They are broken down into glucose, which is then utilized by cells to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell. Proteins, composed of amino acids, are essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes, and supporting immune function. Fats, although often misunderstood, are fundamental for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins and providing essential fatty acids that our bodies cannot produce independently. Each of these macronutrients must be balanced to support metabolic functions effectively.
Vitamins and minerals, categorized as micronutrients, play critical roles in numerous biological processes. Vitamins facilitate energy production, aid in the immune response, and promote cell growth. Minerals, such as calcium and iron, are vital for bone health and oxygen transport in the blood, respectively. The interplay between these nutrients highlights the importance of a balanced diet, as deficiencies in any of them can lead to adverse health outcomes.
Moreover, adequate nutrition is essential for maintaining energy levels, supporting immune health, and promoting physical and cognitive growth, particularly in children. This complex relationship between nutrition and health underscores why understanding nutrition is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Ultimately, a well-rounded approach to nutrition can enhance quality of life and prevent chronic diseases.
A balanced diet is essential for maintaining overall health and wellness, comprising various components that work together to nourish the body. Central to this concept are macronutrients and micronutrients, which are crucial for energy, growth, and bodily functions. Understanding these components and their roles can help individuals make informed decisions about their dietary habits.
Firstly, macronutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, each serving specific functions. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy. They can be classified into simple and complex carbohydrates, with the latter providing sustained energy and contributing to digestive health. It is recommended that carbohydrates make up about 45-65% of total daily calories, focusing on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables for optimal benefits.
Secondly, proteins are vital for repairing tissues, building muscle, and producing enzymes and hormones. They can be sourced from both animal and plant foods. The Dietary Guidelines suggest that proteins should account for about 10-35% of an individual’s calorie intake, emphasizing the importance of including a variety of protein sources, such as lean meats, beans, and legumes.
Lastly, fats, often misconceived as unhealthy, are essential for growth and energy production. They play a role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and are crucial for hormone production. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and fish, should constitute about 20-35% of daily caloric intake. It is essential to limit saturated and trans fats to maintain heart health.
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients—vitamins and minerals—play a significant role in bodily functions, supporting everything from immune function to bone health. Aiming for a diverse diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help ensure adequate intake of these vital nutrients. By balancing these components, individuals can work towards achieving an overall healthy lifestyle.
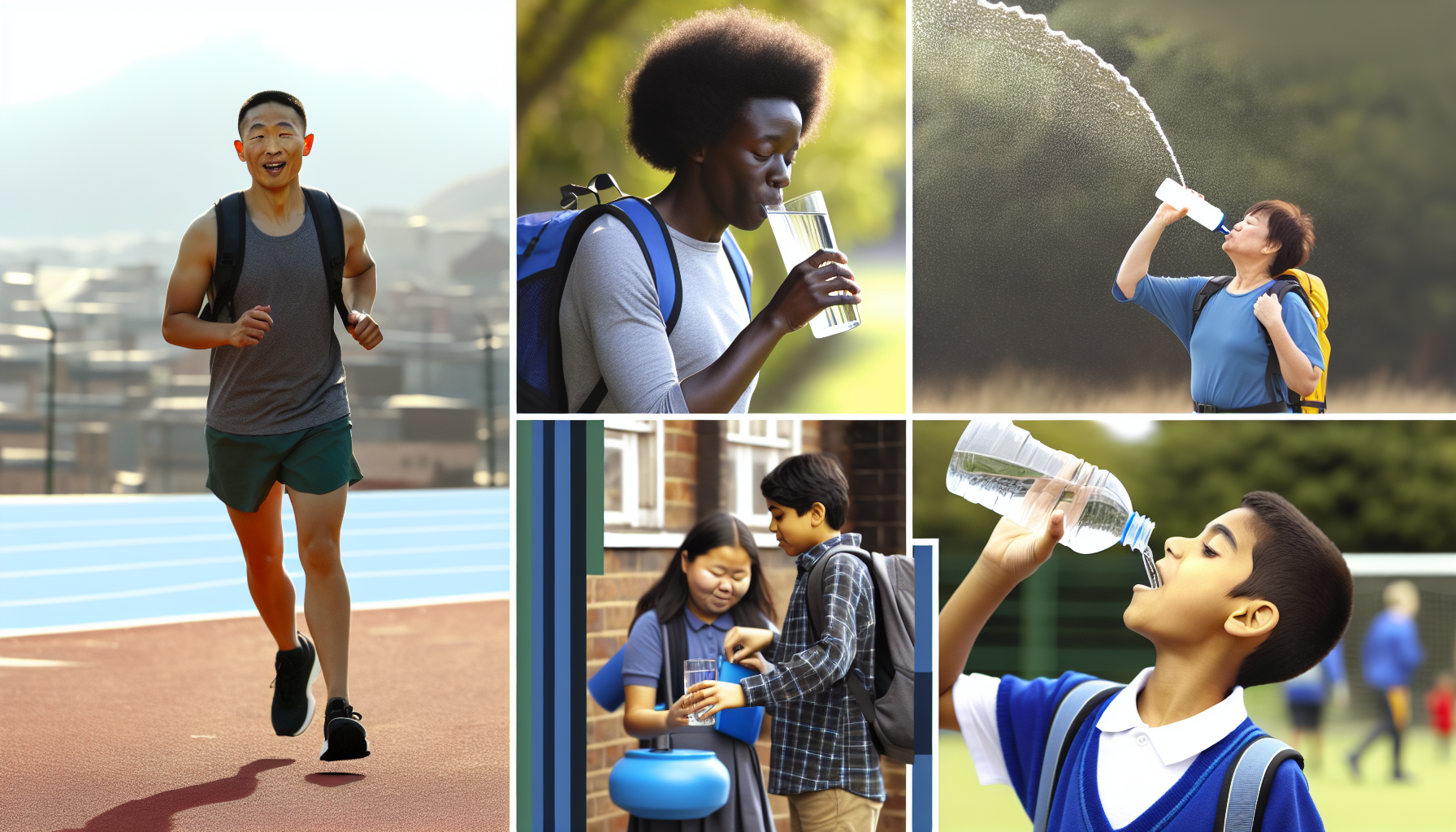
Water is often overlooked in discussions about nutrition, yet it is a vital component that plays an integral role in maintaining overall health. Approximately 60% of the human body is composed of water, underscoring its significance in physiological functions. Staying adequately hydrated is essential for numerous bodily processes including temperature regulation, joint lubrication, and the transportation of nutrients. Moreover, water supports digestion and nutrient absorption, facilitating the breakdown of food and aiding in the delivery of essential vitamins and minerals to cells.
Dehydration can lead to serious health concerns such as fatigue, dizziness, and impaired cognitive functioning. Because water needs can fluctuate based on various factors—such as activity level, age, and environmental conditions—it is crucial to be mindful of one’s hydration status. For instance, individuals engaged in intense physical activities or those living in hot climates may require increased water intake to offset fluid loss through sweat and respiration. In contrast, individuals who are relatively sedentary may have different hydration needs. Recognizing the signs of dehydration, which include thirst, dry mouth, and decreased urine output, is vital for promoting optimal health.
To ensure adequate water intake, individuals can adopt several practical strategies. Carrying a reusable water bottle, setting reminders to drink water throughout the day, and consuming hydrating foods such as fruits and vegetables can significantly enhance hydration levels. Additionally, it is advisable to listen to one’s body, as thirst cues often indicate the need for fluid replenishment. By prioritizing water intake, individuals can not only support their nutritional needs but also enhance their overall well-being.
In the modern grocery landscape, food labels serve as essential tools for consumers seeking to make informed choices about their nutrition. A comprehensive understanding of food labels can empower individuals to select healthier options while shopping. The first step in this process involves grasping the significance of serving sizes. Serving sizes indicate the recommended amount of food that one should consume at one time, which is crucial for assessing caloric intake and portion control. It’s important to be aware that serving sizes may not always align with individual dietary needs, and, therefore, care must be taken to adjust expectations based on personal health goals.
Next, calorie content is pivotal when evaluating food items. Caloric information, typically presented per serving, helps consumers understand the energy they will derive from a particular food. By monitoring calorie intake, individuals can maintain a balanced diet that aligns with their health objectives. Additionally, a focus on the macro and micronutrient breakdown is vital. The nutrition facts panel provides detailed information on essential nutrients such as fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. To promote optimal health, it is advisable to select foods that are rich in essential nutrients while low in unhealthy fats and added sugars.
Another critical component of food labels is the ingredient list. Ingredients are typically listed in descending order by weight, allowing consumers to identify the primary components of a food product. This aspect is particularly useful for those with dietary restrictions or allergies. By scrutinizing this list, one can discern whether a product contains highly processed ingredients or additives. Armed with this knowledge, consumers can make choices that better align with their nutritional preferences. Understanding food labels not only enhances personal health but also fosters a deeper awareness of food quality, ultimately contributing to a balanced diet.
Creating balanced meals is essential for maintaining optimal health and nutrition. A well-structured meal plan incorporates an appropriate mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, alongside vital vitamins and minerals. To begin, understanding the recommended proportions of these macronutrients can provide clarity in designing meals. The general guideline suggests that carbohydrates should make up approximately 45-65% of your total daily intake, proteins should account for 10-35%, and fats should consist of about 20-35%.
To ensure every meal is nutritionally balanced, it is vital to include a variety of food sources. When selecting carbohydrates, opt for whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, as they not only provide energy but also include fiber essential for digestive health. For protein sources, consider lean meats, fish, legumes, and plant-based options like tofu or tempeh. Healthy fats can be obtained from avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Integrating these components into meals can enhance flavor and nutritional value.
Meal planning can streamline the process of creating balanced meals. One practical strategy is to prepare a weekly menu, ensuring that each day includes diverse food choices from each macronutrient group. For instance, a dinner option might feature grilled chicken (protein), steamed broccoli (fiber and vitamins), and quinoa (carbohydrates), drizzled with olive oil (healthy fats). Incorporating colorful fruits and vegetables not only adds variety but also ensures a range of nutrients are consumed.
For those seeking inspiration, consider creating a simple rotating meal schedule. Sample breakfast options could include oatmeal topped with fruit and nuts, while lunch might feature a turkey wrap with spinach and hummus. Snack choices can range from Greek yogurt with berries to a handful of mixed nuts. By employing these actionable strategies, anyone can cultivate a habit of preparing balanced meals that contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Nutrition is often shrouded in misconceptions, with many myths persisting despite scientific advancements. One prevalent myth is that all carbohydrates are harmful and should be avoided for a healthy diet. In reality, carbohydrates are a primary energy source necessary for bodily functions. Instead of eliminating carbs entirely, it is beneficial to distinguish between complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, and simple carbohydrates, like sugary snacks. Prioritizing the former contributes to sustained energy levels and overall health.
Another common misunderstanding lies in the perception of fats. Many individuals believe that consuming any amount of fat leads to weight gain. However, fats play a crucial role in essential bodily functions, including hormone regulation and nutrient absorption. It is important to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fats; while trans and saturated fats should be limited, healthy fats found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil provide significant benefits when consumed in moderation.
Protein is frequently touted as the end-all solution for various health goals, leading to the myth that more protein equates to better health. While protein is essential for muscle repair and overall growth, excessive intake does not necessarily yield additional benefits. Most individuals can achieve their protein requirements through a balanced diet that includes diverse sources such as legumes, dairy, and lean meats. Additionally, individuals with specific health conditions or dietary restrictions may require tailored protein strategies to avoid potential adverse effects from overconsumption.
Furthermore, the dichotomy of “natural” versus “processed” foods often creates confusion. Not all processed foods are detrimental to health; some can be beneficial, offering convenience and essential nutrients. Understanding food labels and recognizing the difference between minimally processed versus heavily processed items can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices.
In conclusion, it is crucial to approach nutrition with a critical mind. By debunking these common myths, individuals are better equipped to navigate through the overwhelming sea of nutritional advice, ultimately making healthier and more informed choices.

Nutritional requirements are not universally applicable; they vary significantly based on factors such as age, gender, and lifestyle. Understanding these differences is crucial for achieving optimal health and wellness. In childhood, for instance, the body requires a balanced intake of macronutrients and micronutrients to support growth and development. Key vitamins, such as vitamin D and calcium, play a vital role in fostering healthy bone development during these formative years. Similarly, adolescents often experience increased caloric and nutritional needs due to rapid growth spurts, necessitating a focus on proteins, iron, and certain vitamins.
As individuals transition into adulthood, nutritional needs may shift based on lifestyle choices and physiological changes. Adult women, for example, may have distinct nutritional considerations related to menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. Men, on the other hand, typically require higher protein intake to support muscle maintenance and metabolism, particularly as they age. Furthermore, both genders should pay attention to their dietary choices to mitigate the risk of chronic diseases such as osteoporosis, heart disease, and diabetes.
In senior years, the body requires a reassessment of nutritional intake. Older adults may face issues such as diminished appetite, difficulty chewing, and nutrient absorption challenges, resulting in a higher risk for deficiencies. Therefore, ensuring a diet rich in nutrients while being mindful of caloric intake is essential. Lastly, it is important to consider the unique nutritional needs of athletes or individuals with chronic health conditions. Athletes may require higher carbohydrates and proteins to fuel their activity, while those with specific health conditions may need tailored dietary modifications to manage their symptoms effectively. Balancing nutritional needs according to age, gender, and lifestyle factors is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Dietary supplements are products designed to enhance the intake of essential nutrients and can play a significant role in a balanced diet. They come in various forms, including vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, and enzymes. While a well-rounded diet ideally provides all necessary nutrients, there are instances where supplements may be beneficial or even necessary. Factors such as age, lifestyle, health conditions, and dietary restrictions can affect nutrient absorption and overall nutritional needs.
For certain populations, including pregnant women, the elderly, and individuals with specific health conditions, dietary supplements can help bridge nutritional gaps. For example, folic acid is recommended for women who are pregnant or trying to conceive to support fetal development. Similarly, older adults often require additional vitamin D and calcium to maintain bone health. In these cases, supplements can be an effective way to prevent deficiencies and support overall health.
However, it is essential to recognize potential drawbacks. Over-reliance on supplements may lead to neglecting whole foods, which offer a complex array of nutrients and bioactive compounds essential for optimal health. Furthermore, some supplements can interact with medications or pose health risks if taken in excessive amounts. Thus, it is crucial to approach supplementation judiciously and prioritize a clean, nutrient-dense diet.
When considering dietary supplements, seeking high-quality products is paramount. Look for certifications from reputable organizations, ensuring that the supplements are tested for purity and potency. Additionally, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen. This step is essential to determine personal nutritional needs, prevent potential side effects, and identify any possible interactions with medications. A well-informed approach to supplementation can complement a balanced diet and contribute to long-term health.
Improving one’s nutrition is a commendable goal that can significantly enhance overall health and well-being. However, the path to a better diet is often filled with challenges, making it essential to set realistic goals that focus on sustainability rather than drastic changes. A common pitfall is attempting to make sweeping changes overnight, which can lead to burnout or discouragement. Instead, embracing gradual adjustments allows individuals to make lasting improvements. For instance, swapping sugary drinks for water or incorporating an additional serving of vegetables into meals can foster healthier habits without overwhelming oneself.
Maintaining motivation is crucial when striving for nutritional enhancement. It is helpful to delineate specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives. These can include goals like preparing home-cooked meals three times a week or gradually reducing sodium intake over several months. By setting such goals, individuals are more likely to stay committed and avoid feeling intimidated by overly ambitious targets. Celebrating small victories along the way, like sticking to a meal plan for a week or trying a new healthy recipe, can further boost enthusiasm.
Tracking progress is another vital component in the journey toward better nutrition. Utilizing food diaries or mobile applications to log meals and snacks can provide insights into eating habits, helping pinpoint areas for improvement. Additionally, periodic self-assessments can allow individuals to evaluate their progress and identify any obstacles encountered. By focusing on creating sustainable habits, one can truly transform their diet over time. Instead of viewing nutrition as a rigid set of rules, approaching it as a flexible framework encourages adaptation and longevity. In conclusion, remember that the journey to improved nutrition is ongoing, and setting realistic goals is key to achieving lasting change.
Looking to advertise, promote your brand, or explore partnership opportunities?
Reach out to us at
[email protected]
Chose where you want to study, and we will let you know with more updates.